

These are then transformed into scale models for wind tunnel testing, with the best developed into upgrades for the car.

This helps them identify the designs with the most potential to gain aerodynamic performance. Before testing a design in the wind tunnel, aerodynamicists run hundreds of different iterations through CFD simulations first. In fact, this is precisely what Formula 1 teams do.

This also ensures that only optimised designs are tested in the wind tunnel, reducing development time. Therefore, aerodynamicists use drag coefficients to compare and optimise the shape of the bodywork to minimise drag.
Drag significantly affects a vehicle's fuel consumption or battery range. ĭrag coefficients are not only useful for comparing different objects, but also different designs of the same object. A typical bird has a Cd of approximately 0.4, while a cow's Cd is around 0.5. You can even compare the drag coefficient between animals. The Toyota Prius has a Cd of around 0.24, while a bus has a Cd between 0.6-0.8. Comparing drag coefficientsĭrag coefficients allow us to compare the aerodynamic efficiency of anything from a car to a building. Whenever you extrapolate a drag force, you need to ensure that the Reynolds number and Mach number of experiments represent reality. At supersonic air flow speeds, shock waves create a significant amount of wave drag, increasing the total drag. The Mach number is the ratio of air velocity to the speed of sound. However, at higher speeds closer to the speed of sound, the Mach number in experiments needs to match the real world. At low air velocities, such as 85m/s (190mph) or approximately 0.25 Mach, the compressibility effects of air are almost non-existent. So if the Reynolds number is not accurately modelled, then the effects of the viscous forces relative to the inertial forces will be unrealistic.Īnother important factor to consider is the compressibility effect of air.
#Air drag skin
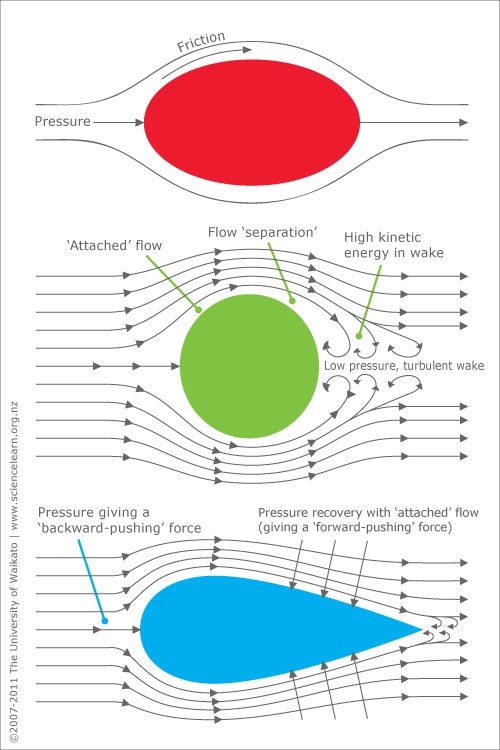
This is because skin friction drag depends on the viscous interaction between the object and the flow. Therefore, to calculate representative drag coefficients, the Reynolds number in experiments has to match reality. How the drag coefficient of a sphere changes with the Reynolds number. Whereas, a flat plate perpendicular to the flow creates a large turbulent wake and increases the drag to 1.1. This shape of object can have a Cd value as low as 0.05. Imagine a teardrop-shaped object, as fluid flows around it, it remains attached to the surface, resulting in minimal drag. As the coefficient of drag is dimensionless, aerodynamicists can easily compare different designs to determine which has the best aerodynamic efficiency. It allows aerodynamicists to model the influence of shape, inclination and flow conditions on aerodynamic drag. The Drag Coefficient Cd quantifies the resistance of an object relative to its frontal area as it moves through a fluid. Calculating the drag coefficient of an airfoil.But what does it mean, how can you measure it, and how can you use it to optimise aerodynamic performance? The coefficient of drag is a common metric used in aerodynamics.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
